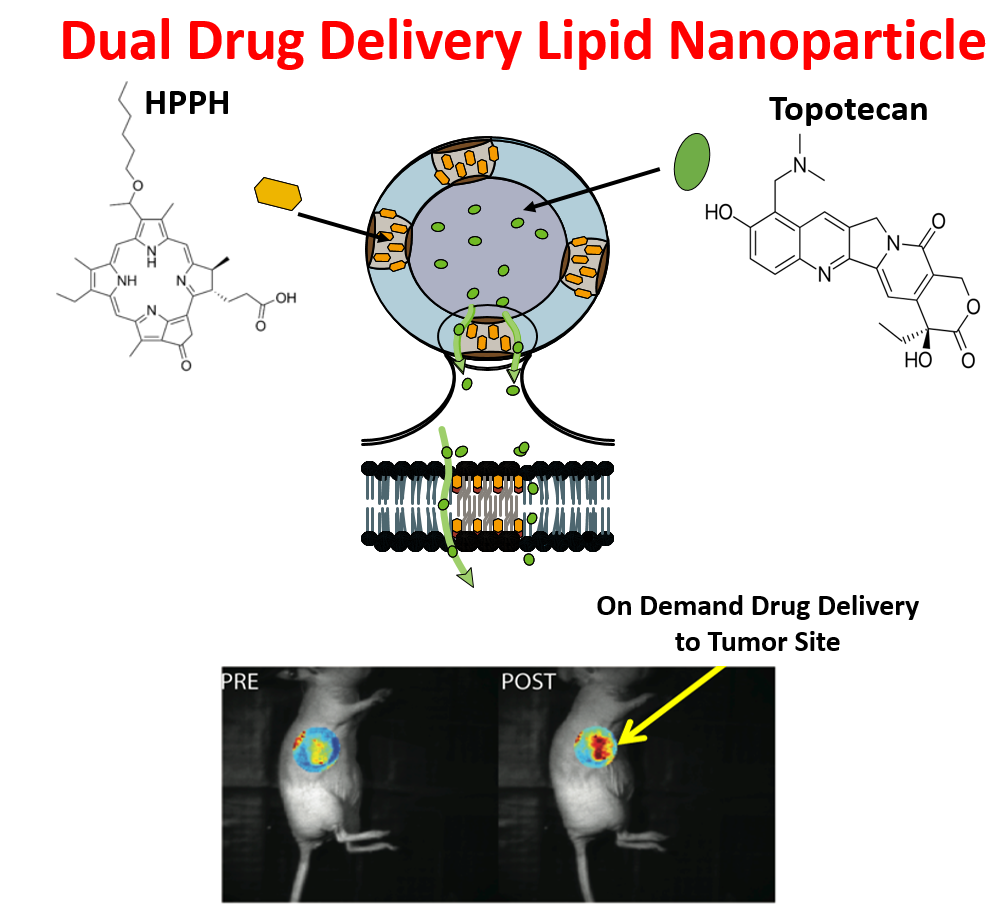
Photoactivatable Lipid-based Nanoparticles as a Vehicle for Dual Agent Delivery
The invention relates to novel lipid-based nanoparticles (liposomes) for use in targeted, on demand and on site drug delivery. The particles include a wall surrounding a cavity, wherein the wall is comprised of:
- A lipid bilayer comprising 1,2-bis(tricosa-10,12-diynoyl)-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine (DC8,9PC), dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC), and 1,2-distearoyl-sn-glycero-3-
phosphoethanolamine-N-[methoxy(polyethylene glycol)-2000] (DSPE-PEG2000), and
- A tetrapyrollic photosensitizer, 2-[1-hexyloxyethyl]-2-devinyl pyropheophorbide-a (HPPH) within the lipid bilayer.
The photosensitive lipid nanoparticles are capable of containing water-soluble agents (e.g., topotecan) in their cavity and designed to be 80-200nm in diameter. The release of agents is triggered by the disruption of the lipid bilayer when light (near-infrared wavelength of 650-670nm) is discretely applied. The concurrent activation of the photosensitizing agent, HPPH may be advantageous in the treatment of certain cancers, especially since this agent possesses therapeutic ability. The inventors have also shown the cytotoxicity of the lipid nanoparticles in T24 bladder cancer cells in the presence and absence of light, drug, and HPPH. The lipid nanoparticles containing the water-soluble agent, topotecan, and HPPH, in the presence of light exhibit superior toxicity as compared to either lipid-nanoparticle encapsulated topotecan or HPPH alone.
Competitive Advantages:
- Stable nanoparticles
- Platform technology applicable to several major, unmet medical needs
- Nanoparticles can be activated upon demand to release a therapeutic agent at a desired site
- The concurrent activation of the photosensitizing agent, HPPH may be advantageous in the treatment of certain types of cancer
- Potential for topical products having shorter time- and cost-to-market; additional licensing opportunities in the cosmetics sector
- Compared with standard emulsions and other types of particle-based delivery, better control of – and prolonged – delivery
- Faster degradation versus particles comprised made from many other polymeric formulations
- Potential for superior tolerability
Commercial Applications:
- The nanoparticles can be used for targeted multiple drug delivery
- Cancer, cardiovascular and musculoskeletal disorders, infectious disease
- Cosmetic/topical products
Patents
- US
Provisional (PRV) 61/845,861
Filed on 2013-07-12
Status: Abandoned - Patent Cooperation Treaty
(PCT) PCT/US2014/045922
Filed on 2014-07-09
Status: Expired - Canada
National Stage 2917545
Filed on 2014-07-09
Status: Issued - European Patent
National Stage 14745037.3
Filed on 2014-07-09
Status: Issued - US Patent 10,117,942
Filed on 2016-01-11
Status: Issued - Switzerland
European patent (EP) 14745037.3
Filed on 2014-07-09
Status: Issued - Germany
European patent (EP) 14745037.3
Filed on 2014-07-09
Status: Issued - France
European patent (EP) 14745037.3
Filed on 2014-07-09
Status: Issued - United Kingdom
European patent (EP) 14745037.3
Filed on 2014-07-09
Status: Issued
Collaborations
- Licensing
- Collaboration